Templating System
This page explains how to use the new templating system and how to make your commands compatible with it. The new system includes parsing of Metadata and Inputs, making command creation and customization easier.
Metadata
Metadata adds extra information to your commands, such as descriptions, tags, categories, and more. This helps users find your commands more easily through template search.
Key Features:
- Improved Discoverability: Makes commands easier to find in the template search.
- JSON Format: Metadata is a JSON object, ensuring structured and error-free information. Incorrect syntax will cause parsing errors.
Metadata Syntax
To add metadata to your code, use the following syntax. Important: Make sure to comment out the metadata in your code; otherwise, it will be treated as a message and sent to the user.
{{{ and }}}
These delimiters mark the beginning and end of the metadata, allowing the system to parse it correctly.
Metadata Structure
Here's the structure of the metadata JSON object:
{{{
"version": number,
"tags": Array<string>,
"author": string,
"usecase": string,
"category": string,
"preview": link,
"description": Array<string>,
"link": Array<link>,
"custommd"?: string // Optional custom markdown
}}}
Explanation of Fields:
version: The version of the command. Use numbers.tags: An array of strings representing keywords related to the command (e.g.,["economy", "balance", "money"]).author: The author of the command (e.g.,"User-0000").usecase: A brief explanation of what the command does (e.g.,"checks the balance of the user").category: The category the command belongs to (e.g.,"economy").preview: A link to a preview image or video demonstrating the command.description: An array of strings providing a detailed description of the command. Each string can be a separate line of the description. Use<code>...</code>to format command examples.link: An array of links to relevant resources, documentation, or examples.custommd: (Optional) A string containing custom markdown to further describe or provide instructions for the command.
Metadata Example
Here's an example of metadata for a !balance command:
/* Metadata :
{{{
"version": "1",
"tags": ["economy", "balance", "money"],
"author": "User-0000",
"usecase": "checks the balance of the user",
"category": "economy",
"preview": "https://media.discordapp.net/attachments/845279377733320745/928401183809364008/unknown.png",
"description": ["Run <code>!bal</code> to show your balance"] ,
"link": ["https://media.discordapp.net/attachments/845279377733320745/928401183809364008/unknown.png"],
"custommd": ""
}}}
*/
The !bal command code
Note: In this example, the link and preview are the same, as it's a simple command.
$onTemplate Function
The $onTemplate function creates a user interface (UI) for interacting with commands. This UI allows users to input values and customize the command before execution. It is especially useful for commands that require user-specific information.
Important: A UI is only generated if the command has associated metadata.
Usage
$onTemplate[type;field;title;help;default value]
Parameters:
type: The type of input field to create.field: The style/appearance of the input field.title: The title displayed above the input field in the UI.help: A helpful description displayed below the input field.default value: The default value for the input field.
Valid Types:
category: Creates a dropdown list of categories from the server.dropdownarrayordropdownshould be used for thefieldparameter.number: Creates a number input field.channel: Creates a dropdown list of channels from the server.dropdownarrayordropdownshould be used for thefieldparameter.role: Creates a dropdown list of roles from the server.dropdownarrayordropdownshould be used for thefieldparameter.text: Creates a single-line text input field.boolean: Creates a checkbox.id: Creates a text input field, typically used for IDs.runonlyin: This modifies the cloned command run only in to the selected channel(s)
Valid Fields:
input: Creates a standard text input field.inputarray: Creates a text input field with the placeholder "Split by ,". The input will be treated as an array, split by commas.dropdown: Creates a dropdown list with values from the specifiedtype. If the type istextornumber, the values are taken from thedefault valueparameter, separated by commas.dropdownarray: Creates a dropdown list where multiple options can be selected. Values are determined as with the standarddropdownfield.checkbox: Creates a checkbox.
Title & Help:
title: The label for the input field.help: A descriptive text providing guidance on what to enter in the input field.
Default Value:
default value: The value that's pre-filled or pre-selected in the input field.
Escaping Special Characters
You cannot use the characters [ ] and ; directly within the $onTemplate function. They are unsupported by the parser.
Use the following escape sequences instead:
#RIGHT#for]#LEFT#for[#SEMI#for;
Example Ticket System
Ticket Code:
$let[categoryID;$onTemplate[category;dropdown;Ticket Category;Choose the category where the ticket should be created;$channelCategoryID]] // Put the category ID Here
$if[$buttonID==openTicket]
$cooldown[1m;<@$authorID> Please Wait %time% to create a new ticket]
$newTicket[$userTag;
{title:🎫 Ticket}
{url:https://raspdevpy.gitbook.io}
{description:You can change this message to yours}
{footer:Press the blue link for the docs}
{button:Close The ticket:red:❌:closeTicket}
{color:RANDOM}
;$get[categoryID];no;Could not Create Ticket]
$elseIf[$buttonID==closeTicket]
$sendMessage[{title: This ticket will be closed in 10s} {color: #ff4a4a};no]
$disableButton[$messageID;closeTicket]
$wait[10s]
$closeTicket[This channel is not a ticket!]
$endelse
Template Asking for Input:
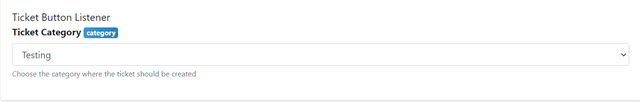
After Cloning: $let[categoryID;866251414232498197]
Special Cases: Arrays
dropdownarray and inputarray fields split their input by commas (,). To use these arrays in your custom commands, you need to spread them.
How to Spread Arrays:
$let[input;input,from,template]
$giveRoles[$authorID;$spread[,;$input]]